New model of irregular heartbeat could boost drug efficacy
Jonathan Silva, a biomedical engineer in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has developed the first computational model that shows the molecular groundwork of a popular drug’s effectiveness in a variety of ways.
Edging closer to personalized medicine for patients with irregular heartbeat
An international team, including faculty from the School of Engineering & Applied Science at Washington University in St. Louis, has used genetic phenotype to determine which patients would benefit the most from a commonly used drug treatment.
Gene testing for heart diseases now available
The School of Medicine now offers genetic testing to help diagnose and treat patients with heart disorders that can lead to sudden death. The new test, offered though the school’s Genomics and Pathology Services (GPS) and developed in collaboration with Washington University cardiologists, analyzes genes linked to arrhythmias and cardiomyopathies.
New math model of heart cell has novel calcium pathway
David Kilper/WUSTL PhotoProfessor Yoram Rudy (center), with Ph.D. student Yong Wang (left) and post-doctroal fellow Leonid Livshitz (right), with their ECGI system on a mannequin, comment on the cardiac data.Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis have developed the first mathematical model of a canine cardiac cell that incorporates a vital calcium regulatory pathway with implications for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats. Thomas J. Hund, Ph.D., post-doctoral researcher in Pathology ( in Dr. Jeffrey Saffitz laboratory) at the Washington University School of Medicine, and Yoram Rudy, The Fred Saigh Distinguished Professor of Engineering at Washington University, have incorporated the Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II (CaMKII) regulatory pathway into their model, improving the understanding of the relationship between calcium handling in cardiac cells and the cell’s electrical activity.
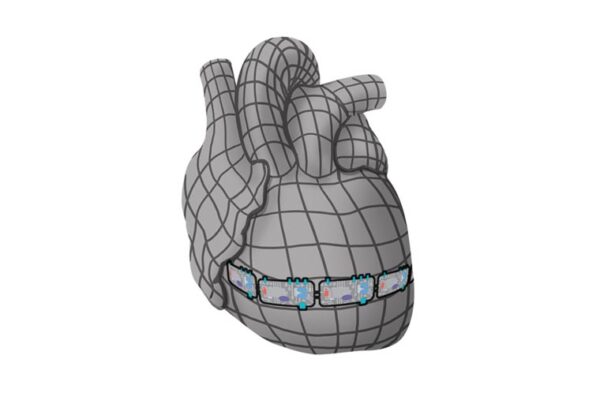
Disrupting the ‘heart’s tornado’ in arrhythmia
A biomedical engineer at WUSTL has determined love taps are better than love jolts in addressing defibrillation.When it comes to affairs of the heart, love taps are preferred over love jolts. That is the result of a team of heart researchers including Igor Efimov, Ph.D., associate professor of biomedical engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, trying to effect a better implantable heart defibrillator. Efimov and his colleagues have modeled a system where an implantable heart defibrillator focuses in on rogue electrical waves created during heart arrhythmia and busts up the disturbance, dissipating it and preventing cardiac arrest.