Warming alters predator-prey interactions in the Arctic
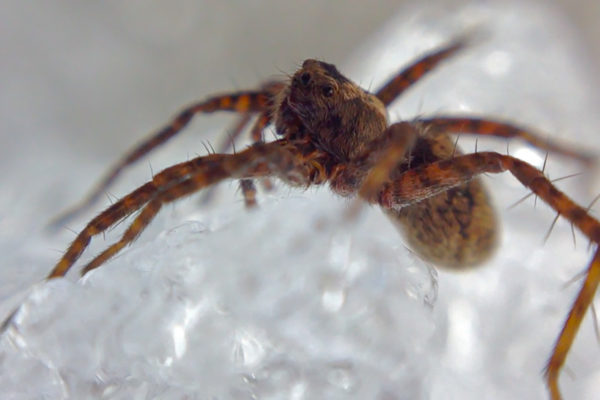
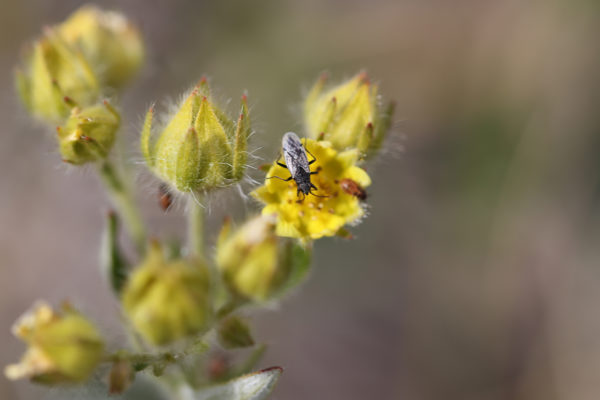
Under warming conditions, Arctic wolf spiders’ tastes in prey might be changing, according to new research by biologist Amanda Koltz in Arts & Sciences — initiating a new cascade of food web interactions that could potentially alleviate some impacts of global warming.
Researchers engineer bacteria that create fertilizer out of thin air
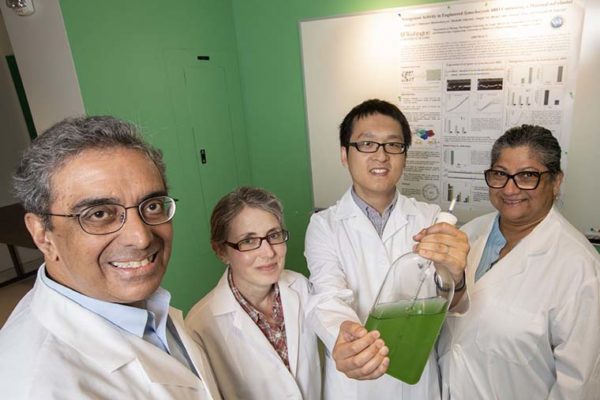
A team at Washington University in St. Louis has created a bacteria that uses photosynthesis to create oxygen during the day, and at night, uses nitrogen to create chlorophyll for photosynthesis. This development could lead to plants that do the same, eliminating the use of some — or possibly all — man-made fertilizer, which has a high environmental cost.
Courage in the face of climate change
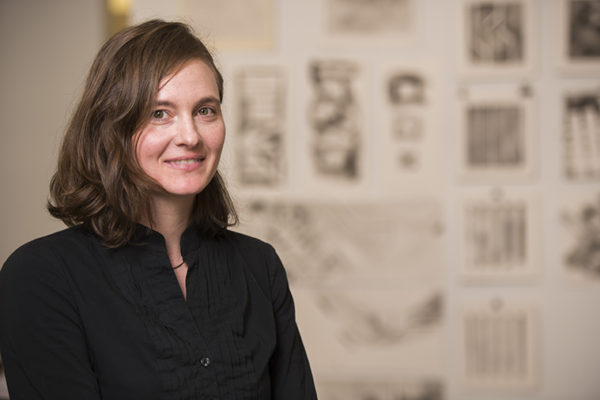
Thirty years ago this month, the term global warming became part of our popular conversation. Doctoral candidate Andrea Godshalk from the Sam Fox School of Design & Visual Arts reflects on the recent Saint Louis Climate Summit and the challenge of re-imagining key infrastructure, systems and values.
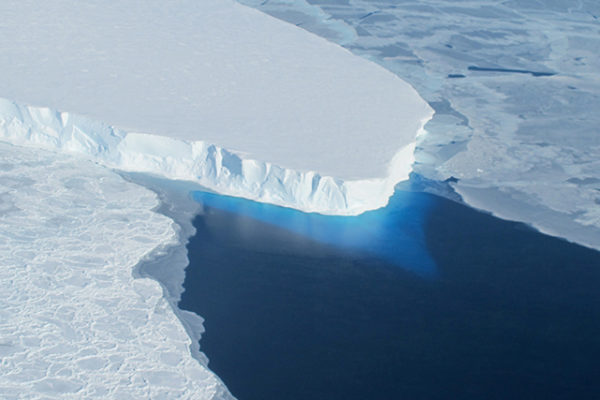
Bedrock in West Antarctica rising at surprisingly rapid rate
The findings, reported in the journal Science, contain positive implications for the survival of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which scientists had previously thought could be doomed because of the effects of climate change, according to study co-author Douglas Wiens of Arts & Sciences.
Bugged out by climate change
Warmer summer and fall seasons and fewer winter freeze-thaw events have led to changes in the relative numbers of different types of bugs in the Arctic, says Amanda Koltz, a postdoctoral fellow in Arts & Sciences. The study relies on the longest-standing, most comprehensive data set on arctic arthropods in the world today: a catalogue of almost 600,000 flies, wasps, spiders and other creepy-crawlies collected at the Zackenberg field station on the northeast coast of Greenland from 1996-2014.
Faculty, students participate in climate summit April 22-24
Washington University faculty and students will moderate panels at the Saint Louis Climate Summit, hosted by Saint Louis University. Students, faculty and staff can attend an evening with Bill Nye of “Science Guy” fame and environmentalist Carl Pope on April 23 for free by showing their IDs at the ticket booth.
Global warming focus of 2018 McDonnell lecture
S. George Philander, one of the world’s leading experts on climate and the interactions between the ocean and atmosphere, will deliver two talks March 28 and 29 as part of the McDonnell Distinguished Lecture Series, sponsored by Washington University in St. Louis’ McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences.
WashU Expert: Trump’s withdrawal from Paris Agreement a play to his base
President Donald Trump has made the decision to pull the U.S. out of the 2015 Paris climate agreement, a move that that cannot be justified on the stated grounds for withdrawal, says an expert in environmental law at Washington University in St. Louis.
Death by volcano?
The discovery of anomalously high levels of mercury in rocks from the Ordivician geological period has led to a new interpretation of the ensuing mass extinction. A sequence of disturbances may have led to catastrophic cooling by reflective sulfate aerosols injected into the atmosphere by massive volcanism. The finding is important since aerosol cooling is under consideration as a way to temper global warming.
Climate change: Are we there yet?
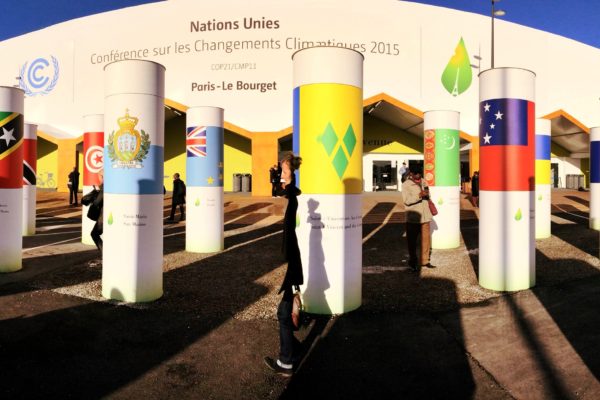
The six Washington University students who went to the Conference of the Parties (COP21) climate negotiations in Paris are well prepared, resilient, tough-minded and in this fight for the duration.
View More Stories