Food culture along the Silk Road
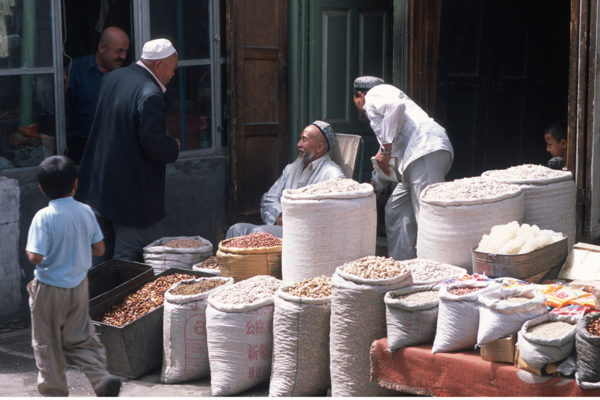
Like passionate foodies who know the best places to eat in every town, Silk Road nomads may have been the gastronomic elites of the Medieval Ages, enjoying diets much more diverse than their sedentary urban counterparts, suggests a new study in Scientific Reports.
Mimicking diet changes of global travel reveals clues to gut health
With the growing understanding of the importance of gut bacteria in human health, researchers at the School of Medicine studied gut motility, measuring the transit time of food moving through the gastrointestinal tract in mice in a way that mimicked the dietary effects of world travel. The study demonstrates ways to uncover how even a single ingredient, such as turmeric, can affect health through interactions of diet and gut microbes.
A person’s diet, acidity of urine may affect susceptibility to UTIs
The acidity of urine — as well as the presence of small molecules related to diet — may influence how well bacteria can grow in the urinary tract, a new study shows. The research, led by Jeffrey Henderson, MD, PhD, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, may have implications for treating urinary tract infections, which are among the most common bacterial infections worldwide.
Exercise for older mouse mothers lowers risk of heart defects in babies
Older mice genetically prone to bear offspring with heart defects can reduce this risk to that of younger mouse mothers with the same genetic defect through exercise alone, according to new research at the School of Medicine. The study, led by Patrick Y. Jay, MD, PhD, also suggests that the increased risk of congenital heart defects is tied to the age of the mother and not the age of her eggs.
Cutting phosphate in diet reduces deaths, heart problems related to kidney disease
Severely
restricting dietary phosphate early in the course of chronic kidney
disease can prevent related heart and vascular problems, a new study in rats indicates. Phosphate, an essential mineral, is found in colas, milk, cheese and other dairy products, beans and high-protein foods, and often is added as a preservative in processed foods.
Altering mix of gut microbes prevents obesity, but diet remains key factor
The mix of microbes living inside the gut can protect against obesity, but a healthy diet is critical, according to School of Medicine scientists who transplanted intestinal microbes from obese and lean twins into mice and fed the animals different diets. Pictured are researchers Vanessa Ridaura, a graduate student, and Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, director of the Center for Genome Sciences and Systems Biology.
How to have a healthy holiday: The key is balance
There’s nothing wrong with a cookie or a glass of eggnog at the holidays, says Debra Haire-Joshu, PhD, director of the Center for Obesity Prevention and Policy Research and the Center for Diabetes Translation Research at Washington University in St. Louis and associate dean for research at the Brown School. The key, Haire-Joshu says, is balance.
Folic acid may reduce some childhood cancers
Folic acid fortification of foods may reduce the incidence of the most common type of kidney cancer and a type of brain tumors in children, finds a new study by Kimberly J. Johnson, PhD, assistant professor at the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis, and Amy Linabery, PhD, postdoctoral fellow at the University of Minnesota. Incidence reductions were found for Wilms’ tumor, a type of kidney cancer, and primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNET), a type of brain cancer.
Direct link found between diet ingredients and gut microbes
Two new studies showcase the dynamic relationship between components of the diet and the intestinal microbiome. The research provides a foundation for improving human health by designing diets and foods that enhance microbes’ ability to capture specific food ingredients or that enrich the presence of beneficial microbes.
Diet-exercise combo best for obese seniors
For obese seniors, dieting and exercise together are more effective at improving physical performance and reducing frailty than either alone. Although weight loss alone and exercise alone improve physical function, neither is as effective as diet and exercise together, which improved physical performance in seniors by 21 percent.
View More Stories