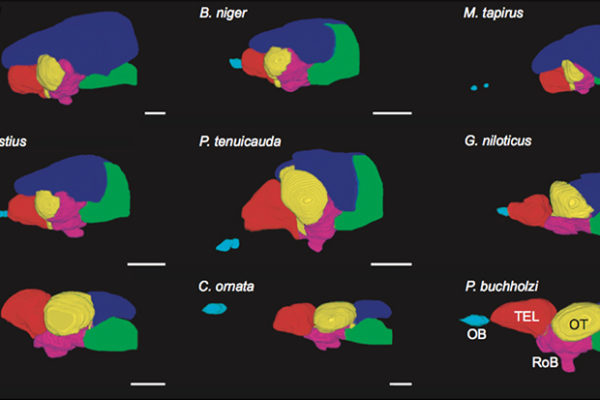
New maps hint at how electric fish got their big brains
Washington University researchers have mapped the regions of the brain in mormyrid fish in extremely high detail. In a study published in the Nov. 15 issue of Current Biology, they report that the part of the brain called the cerebellum is bigger in members of this fish family compared to related fish — and this may be associated with their use of weak electric discharges to locate prey and to communicate with one another.
Jump in communication skills led to species explosion among electric fishes
The Mormyridae, a family of African fishes that communicate by means of weak electic discharges, has more than 200 species. Given its diversity a Washington University in St. Louis biologist wondered whether changes in electric communication might have influenced rates of speciation. His work showed that the fishes evolved a complex signal-processing brain before a burst of speciation, that signal variation was higher among fishes with that brain, and that these fishes could distinguish among subtly different discharges, whereas others could not.Together it adds up to a strong case for brain evolution triggering increased diversification.