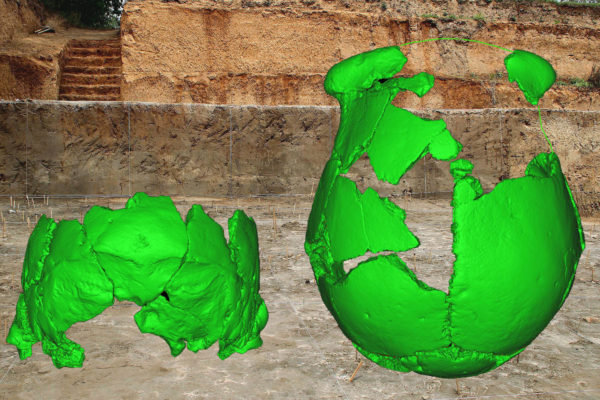
What 100,000-year-old human skulls are teaching us
Two partial archaic human skulls, from the Lingjing site, Xuchang, central China, provide a new window into the biology and populations patterns of the immediate predecessors of modern humans in eastern Eurasia. Securely dated to about 100,000 years ago, the Xuchang fossils present a mosaic of features.
Redating of the latest Neandertals in Europe
TrinkausTwo Neandertal fossils excavated from Vindija Cave in Croatia in 1998, believed to be the last surviving Neandertals, may be 3,000-4,000 years older than originally thought. An international team of researchers, including Erik Trinkaus, Ph.D., the Mary Tileston Hemenway Professor of anthropology in Arts & Sciences, has redated the two Neandertals from Vindija Cave, the results of which have been published in the Jan. 2-6 early edition of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).