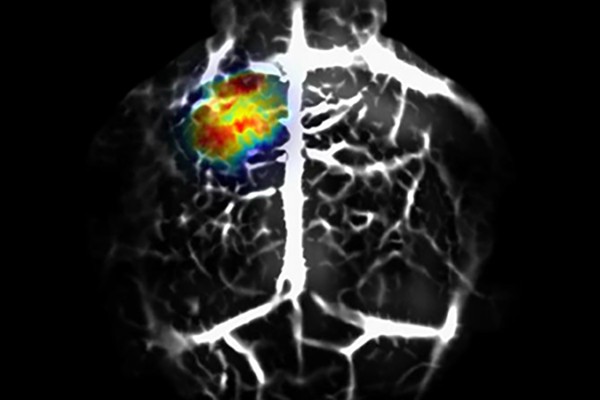
Flipping the switch to better see cancer cells at depths
A team of engineers, led by Washington University’s Lihong Wang and postdoctoral researcher Junjie Yao, found that by genetically modifying glioblastoma cancer cells to express BphP1 protein, derived from a bacterium commonly found in soil and water, they could clearly see tiny amounts of live cancer cells as deep as 1 centimeter in tissue using photoacoustic tomography.
$3.8 million NIH grant funds WUSTL brain imaging center
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have received a five-year, $3.8 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke to renew a center that helps researchers collect and use data on the brain and central nervous system.
Ultrasound imaging on smartphone may change global medicine
WUSTL computer engineers are bringing the minimalist approach to medical care and computing by coupling USB-based ultrasound probe technology with a smartphone, enabling a compact, mobile computational platform and a medical imaging device that fits in the palm of a hand.
Ultrasound imaging now possible with a smartphone
David Kilper/WUSTL PhotoComputer engineers at Washington University in St. Louis are bringing the minimalist approach to medical care and computing by coupling USB-based ultrasound probe technology with a smartphone, enabling a compact, mobile computational platform and a medical imaging device that fits in the palm of a hand. William D. Richard, Ph.D., associate professor of computer science and engineering, and David Zar, research associate in computer science and engineering, have made commercial USB ultrasound probes compatible with Microsoft Windows mobile-based smartphones, thanks to a $100,000 grant Microsoft awarded the two in 2008.
Novel technique changes lymph node biopsy procedure for breast cancer patients
David Kilper/WUSTL PhotoFor the first time, WUSTL scientists have used gold nanocages to map sentinel lymph nodes in a rat noninvasively using photoacoustic tomography.
Novel technique changes lymph node biopsy, reduces radiation exposure in breast cancer patients
David Kilper/WUSTL PhotoWUSTL biomedical engineers Younan Xia (left) and Lihong Wang examine the photoacoustic tomography machine (PAT) in Wang’s Whitaker Building laboratory.Information obtained from a new application of photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is worth its weight in gold to breast cancer patients. For the first time, Lihong Wang, Ph.D., Gene K. Beare Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, with a joint appointment in Radiology, and Younan Xia, Ph.D., James M. McKelvey Professor in Biomedical Engineering, with a joint appointment in chemistry in Arts & Sciences, both at Washington University in St. Louis, have used gold nanocages to map sentinel lymph nodes (SLN) in a rat noninvasively using PAT.
Nanoparticles offer new hope for cancer detection, treatment
Magnified nanoparticlesSpecially designed nanoparticles can reveal tiny cancerous tumors that are invisible to ordinary means of detection, according to a study by researchers at the School of Medicine. Researchers demonstrated that very small human melanoma tumors growing in mice — indiscernible from the surrounding tissue by direct MRI scan — could be “lit up” and easily located. Because the nanoparticles can be engineered to carry a variety of substances, they also may be able to deliver cancer-fighting drugs to malignant tumors.
Nanoparticles offer new hope for detection and treatment
Magnified nanoparticlesSpecially designed nanoparticles can reveal tiny cancerous tumors that are invisible to ordinary means of detection, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Researchers demonstrated that very small human melanoma tumors growing in mice — indiscernible from the surrounding tissue by direct MRI scan — could be “lit up” and easily located. Because the nanoparticles can be engineered to carry a variety of substances, they also may be able to deliver cancer-fighting drugs to malignant tumors.