Could there be life in Pluto’s syrupy sea?
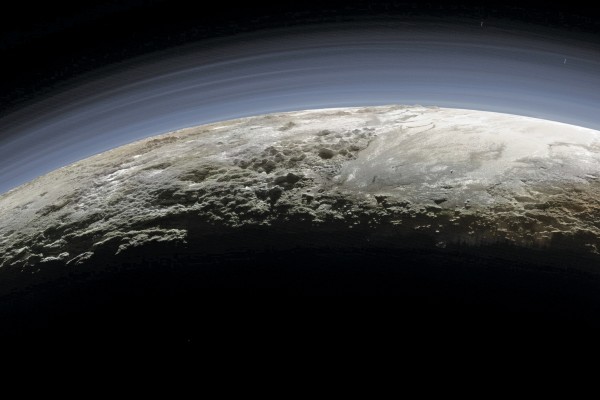
Pluto is thought to possess a subsurface ocean, which is not so much a sign of water as it is a tremendous clue that other dwarf planets in deep space also may contain similarly exotic oceans, naturally leading to the question of life, said one co-investigator with NASA’s New Horizon mission to Pluto and the Kuiper Belt.
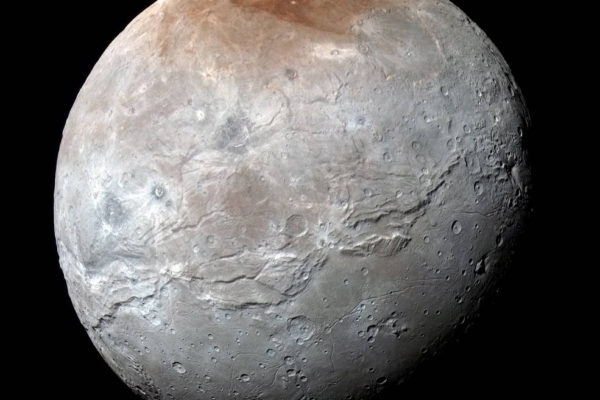
The realms of Mordor
What gives Mordor Macula, the red dusted polar region of Pluto’s moon Charon, its color? New Horizons scientists, including Washington University’s Bill McKinnon, answer the question in the current issue of Nature.
Pluto: A cosmic lava lamp
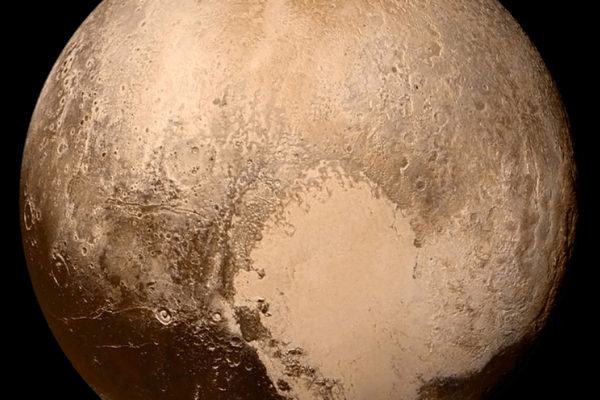
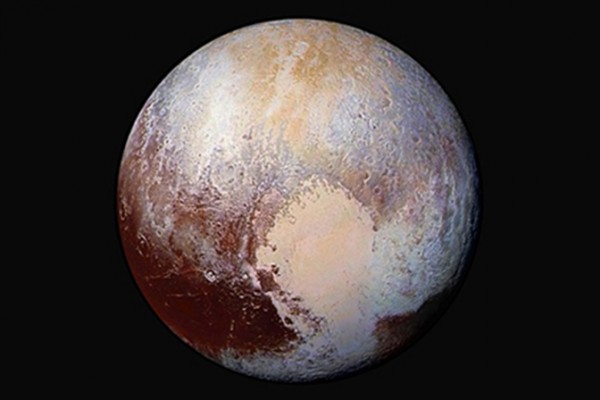
Using computer models, New Horizons team members have been able to determine the depth of the layer of solid nitrogen ice within Pluto’s distinctive “heart” feature — a large plain informally known as Sputnik Planum — and how fast that ice is flowing. “For the first time, we can really determine what these strange welts of the icy surface of Pluto really are,” said William B. McKinnon, who led the study.
Discovering new horizons
After a nearly 10-year wait, planetary scientist William McKinnon, PhD, provides an inside look at New Horizons’ spectacular flyby of Pluto and its first discoveries coming into focus.
A bumper sticker inspires
While at Washington University, Kelsi Singer noticed Bill McKinnon’s bumper sticker, “My other vehicle is on its way to Pluto.” Today, she works on the New Horizons mission and has her own sticker: “My other vehicle explored Pluto.”
It’s alive, it’s alive!
It was bedlam at mission control when the first images of Pluto came down over the Deep Space Network. Not only were there few craters, but some areas of the planet were smooth as a billiard ball and others rumpled and rippled; some stained the color of dried blood and others gleaming bright white. The variety meant that there was geology on Pluto, alien though the
geological processes might be to earthlings.
Rough guide to Pluto-watching with Bill McKinnon
New Horizons will fly through the Pluto system on July 14 at an angle of 46 degrees to the plane of the dwarf planet’s orbit, then turn to use sunlight reflected from Charon, Pluto’s biggest moon, to image areas of Pluto now in continuous darkness. Your host for the WashU Pluto watching party will be Bill McKinnon, a planetary scientist at Washington University in St. Louis, who will be commenting from mission headquarters at the Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory in Maryland.
Coming soon: First encounter with a new class of worlds
After an epic journey across the breadth of the solar system, the New
Horizons spacecraft is finally nearing its destination: the Pluto system, a staggering three billion miles from Earth. William McKinnon, a planetary scientist at Washington University in St. Louis, explains that our understanding of Pluto has been transformed in the nearly 10 years the probe has been en route to its target.