Unnecessary testing for UTIs cut by nearly half
Over-testing for urinary tract infections (UTIs) leads to unnecessary antibiotic use, which spreads antibiotic resistance. Infectious disease specialists at the School of Medicine made changes to hospital procedures that cut urine tests by nearly half without compromising doctors’ abilities to detect UTIs.
Vaginal bacteria can trigger recurrent UTIs, study shows
About half of all women will experience urinary tract infections in their lifetimes, and despite treatment, about a quarter will develop recurrent infections within six months of initial infection. A new study at the School of Medicine has uncovered a trigger of recurrent UTI infections: a type of vaginal bacteria that moves into the urinary tract.
Estrogen fights urinary infection in mouse study
Estrogen levels drop dramatically in menopause, a time when the risk of urinary tract infections increases significantly. Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
have found new evidence in mice that the two phenomena are connected by
more than just timing.
$5.3 million boosts research to fight urinary infections
Researchers at the School of Medicine have received a five-year, $5.3 million grant to explore
the way gender and age influence susceptibility to urinary tract
infections, one of the most common bacterial infections.
Bear Cub grants awarded
Washington University in St. Louis has awarded five Bear Cub fund grants totaling $190,000 to support innovative research that has shown commercial potential. Jerry Morrissey (right), PhD, received one of the grants to develop rapid tests for the early development of kidney cancer.
Immune system overreaction may enable recurrent urinary tract infections
The immune system may open the door to recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) by overdoing its response to an initial infection, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found.
Bacterial target may be ideal for new drug treatments
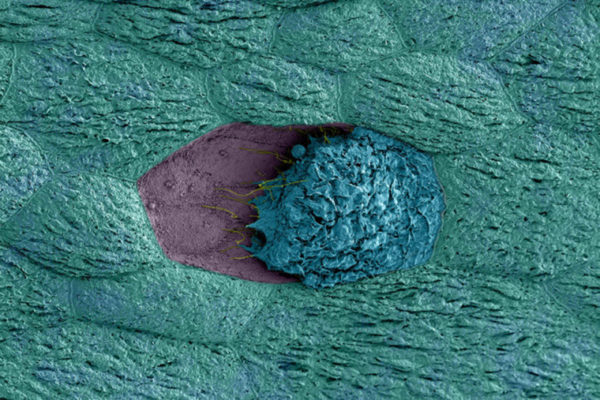
E. Coli (yellow) attaches to a host cell using sticky fibersNew insights into the bacteria responsible for urinary tract infections appear to open up an opportunity for disabling a wide range of infectious bacteria. Researchers at the School of Medicine recently revealed how a protein known as PapD helps E. coli assemble sticky fibers called pili that allow the bacterium to latch onto and infect host cells. Scientists are using what they’ve learned to begin designing pilicides, new treatments that stop pili formation and disrupt the infection process.
Bacterial target may be ideal for new drug treatments
E. Coli (yellow) attaches to a host cell using sticky fibersNew insights into the bacteria responsible for urinary tract infections appear to open up an opportunity for disabling a wide range of infectious bacteria. Researchers at the School of Medicine recently revealed how a protein known as PapD helps E. coli assemble sticky fibers called pili that allow the bacterium to latch onto and infect host cells. Scientists are using what they’ve learned to begin designing pilicides, new treatments that stop pili formation and disrupt the infection process.