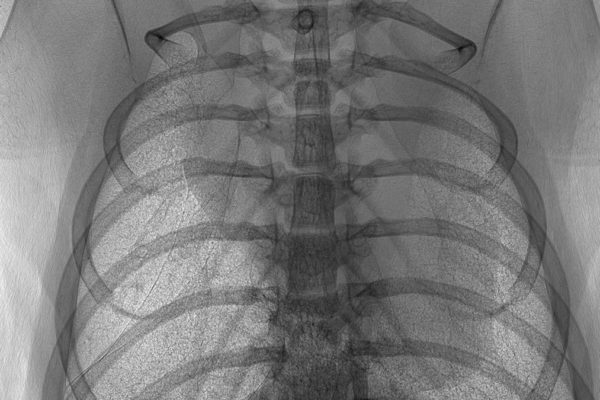
A better look at the lungs
The National Institutes of Health awarded a biomedical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis a 4-year, $1.7 million grant to attempt to develop a new way to image airflow in lungs. The research could someday make diagnoses of lung disease easier and more cost-effective.
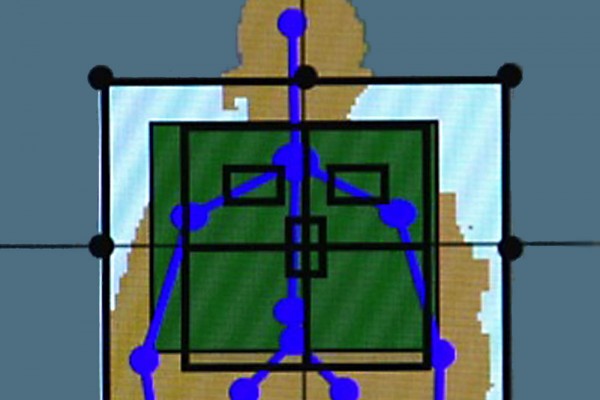
Xbox gaming technology may improve X-ray precision
With the aim of producing high-quality X-rays with minimal radiation exposure, researchers at the School of Medicine have developed a new approach to imaging patients. Using proprietary software developed for the Microsoft Kinect system, the team has adapted hands-free technology used for the popular Xbox system to aid radiographers when taking X-rays.
Chest X-rays don’t reduce lung cancer deaths
A major U.S. study shows that annual chest X-rays to screen for lung cancer do not reduce the risk of dying from the disease, even in smokers or former smokers. More than 150,000 older Americans were involved in the clinical trial, funded by the National Cancer Institute, with about 16,000 enrolled at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Results of the study will be published Nov. 2 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
CT screening reduces lung-cancer deaths in heavy smokers
In a study of heavy smokers, fewer screened with low-dose CT scans died, compared with similar smokers screened with standard chest X-rays. The National Cancer Institute ran the 33-center National Lung Screening Trial to learn whether more sensitive screening could have an impact on lung-cancer deaths, and Washington University researchers involved in the study say it did.