Metabolomics for the masses
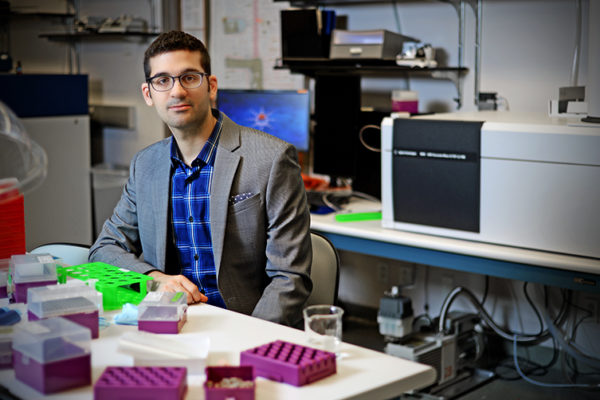
Gary Patti, the Michael and Tana Powell Professor of Chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, has been awarded $4.8 million in two separate National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants focused on improving the accessibility of metabolomics — the study of the biochemical reactions that underlie metabolism.
Epigenome orchestrates embryonic development
Studying zebrafish embryos, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown that the epigenome plays a significant part in guiding development in the first 24 hours after fertilization. The research may deepen understanding of congenital defects and miscarriage.
Scientists find gene vital to central nervous system development
Using Washington University’s state-of-the-art zebrafish facility, scientists have identified a gene that helps regulate how well nerves of the central nervous system are insulated. The finding may have implications for human diseases such as multiple sclerosis, in which this insulation is lost.
Likely culprit in spread of colon cancer identified
New research at the School of Medicine and Vanderbilt University Medical Center has implicated a poorly understood protein called PLAC8 in the spread of colon cancer.
Washington People: Lilianna Solnica-Krezel
Growing up in the picturesque town of Sandomierz in southeastern Poland, Lilianna Solnica-Krezel, PhD, was a serious student and an uncommonly avid reader. Today, Solnica-Krezel, professor and head of the Department of Developmental Biology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is a leading expert in understanding the earliest stages of life’s development.
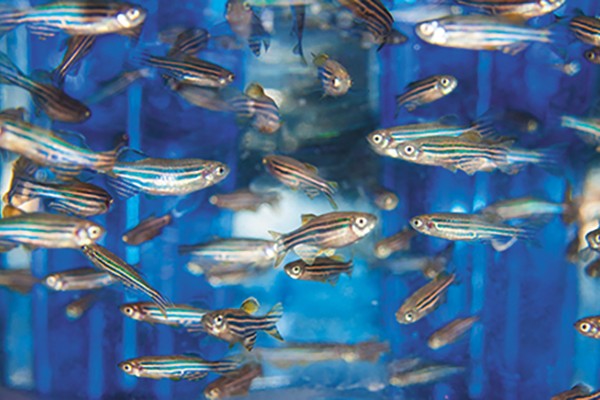
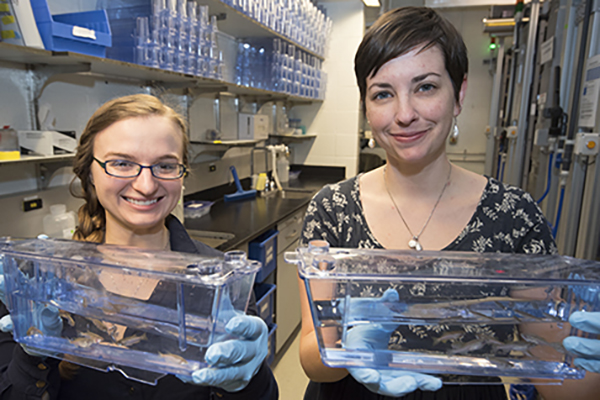
Washington University opens world’s most modern zebrafish facility
Tiny tropical fish are helping scientists understand human development and disease, from birth defects and cancer to muscle and nerve disorders. Contributing to this effort, Washington University is now home to one of the largest zebrafish facilities in the world. And with robotic feeding and cleaning systems, it is the world’s most modern.
Zebrafish regrow fins using multiple cell types, not identical stem cells
What does it take to regenerate a limb? Biologists have long thought that organ regeneration in animals like zebrafish and salamanders involved stem cells that can generate any tissue in the body. But new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has shown that the individual cells in a regenerating limb retain their original identities and only give rise to more of their own kind.
Sugar required for healthy brain development
ZebrafishTo learn more about how glucose affects human development, Washington University researchers have developed the first vertebrate model of the role of glucose in embryonic brain development. The model is made up of zebrafish. Their transparent embryos develop similarly to humans, except that they grow outside of the mother’s body, where development can be more easily observed. The model provides the foundation for and insight into the roles of nutrition and genetics in human birth defects.
Research finds sugar required for healthy brain development
ZebrafishTo learn more about how glucose affects human development, Washington University researchers have developed the first vertebrate model of the role of glucose in embryonic brain development. The model is made up of zebrafish. Their transparent embryos develop similarly to humans, except that they grow outside of the mother’s body, where development can be more easily observed. The model provides the foundation for and insight into the roles of nutrition and genetics in human birth defects. The research also may have implications for patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s. More…