Engineers develop new fuel cells with twice the operating voltage as hydrogen fuel cells
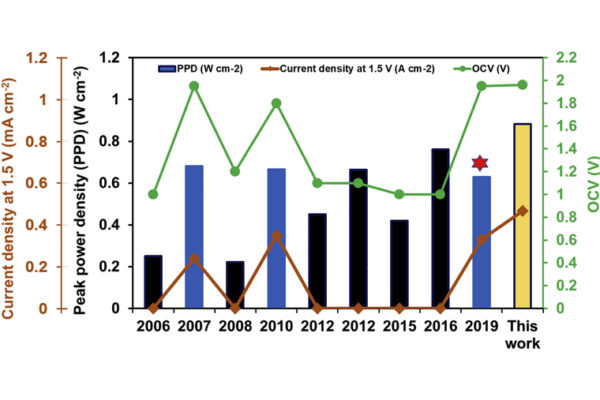
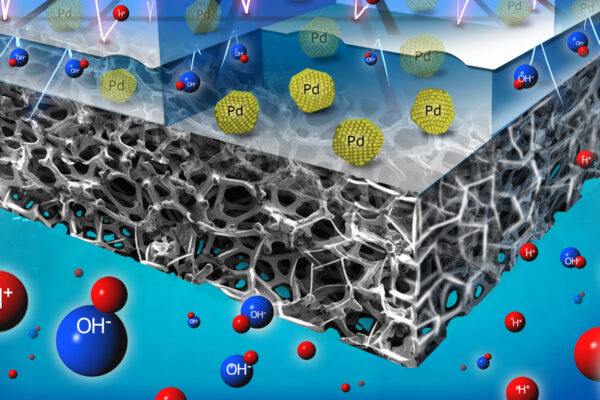
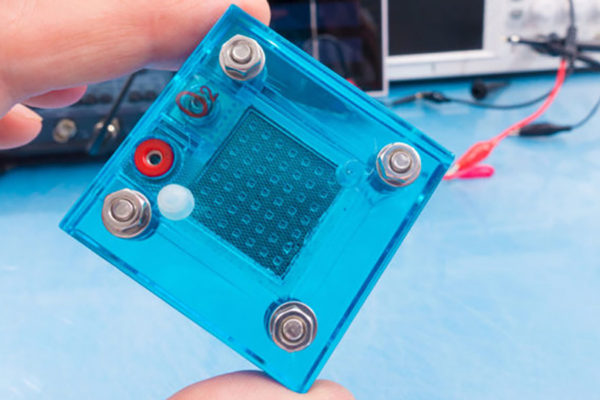
Engineers at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis have developed high-power, direct borohydride fuel cells that operate at double the voltage of conventional hydrogen fuel cells.
Advancing the capability of high-powered fuel cells
A team of engineers in the McKelvey School of Engineering has developed a high-powered fuel cell that operates at double the voltage of today’s commercial fuel cells. It could power underwater vehicles, drones and eventually electric aircraft at a significantly lower cost.
Creating longer-lasting fuel cells
Fuel cells could someday generate electricity for nearly any device that’s battery-powered, including automobiles, laptops and cellphones. An engineering team at Washington University in St. Louis has developed a new way to take a look inside these fuel cells, in an effort to extend their lifespans.
New catalyst could boost cleaner fuel use
Younan XiaMaterial scientists at Washington University in St. Louis have developed a technique for a bimetallic fuel cell catalyst that is efficient, robust and two-to-five times more effective than commercial catalysts. The novel technique eventually will enable a cost effective fuel cell technology, which has been waiting in the wings for decades and should give a boost for cleaner use of fuels worldwide.
Create one, teach one
David Kilper/WUSTL Photo ServicesThe combination of beer, wastewater, microbes, fuel cells, high-school students and teachers sounds like a witches’ brew for an old-fashioned, illicit 1960s beach party. Instead, these are the components of a new high-school science curriculum being developed by researchers at Washington University and two St. Louis area high-school teachers.
Create one, teach one
David Kilper/WUSTL Photo ServicesThe combination of beer, wastewater, microbes, fuel cells, high-school students and teachers sounds like a witches’ brew for an old-fashioned, illicit 1960s beach party. Instead, these are the components of a new high-school science curriculum being developed by researchers at Washington University and two St. Louis area high-school teachers.
Microbial fuel cells turn on the juice
David Kilper/WUSTL PhotoLars Angenent, Ph.D., assistant professor of energy, environmental & chemical engineering, with a microbial fuel cell.The combination of beer, wastewater, microbes, fuel cells, high school students and teachers sounds like a witches’ brew for an old-fashioned, illicit ’60s beach party. Instead, these are the components that comprise the heart and soul of a new high school science curriculum being developed by researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and a couple of St. Louis area high school teachers. Video available.
Patented device uses bacteria to create electricity, treat wastewater
Photo by David KilperLars Angenent (right) and Jason He examine the upflow microbial fuel cell, which can turn wastewater into electricity.The upflow microbial fuel cell is fed continually and works with chambers atop each other rather than beside each other.
Patented device creates electricity and treats wastewater
David Kilper / WUSTL PhotoAngenent and He’s microbial fuel cell may be scaled up for industrial use.An environmental engineer at Washington University in St. Louis has created a device similar to a hydrogen fuel cell that uses bacteria to treat wastewater and create electricity. Lars Angenent, Ph.D., assistant professor of Chemical Engineering, and a member of the University’s Environmental Engineering Science Program, has devised a microbial fuel cell which he calls an upflow microbial fuel cell (UMFC) that is fed continually and, unlike most microbial fuel cells, works with chambers atop each other rather than beside each other.