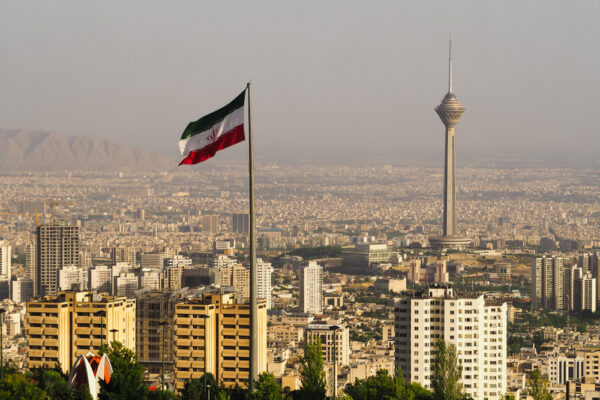
WashU Expert: Soleimani killing likely unlawful
Many questions remain following the Jan. 3 death of Qassem Soleimani and Iran’s potential retaliation. Chief among them: Was the strike legal? “Unless there is much more to the story than meets the eye, the answer seems to be no,” said Leila Sadat, director of the Whitney R. Harris World Law Institute and an expert on international criminal law.
WashU Expert: Syrian air strikes not in line with international law
Although one can fault the Obama administration for its tepid policy towards Syria, President Donald Trump’s April 6 air strikes against a Syrian military base take the U.S. policy towards Syria to a new low, said an expert on international war crimes at Washington University in St. Louis.
WashU Expert: Congress should work with Obama to close Gitmo
President Barack Obama this week announced his intention to close the detention facility at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba. The decision to open the facility in the first place was a bad idea in theory, made even worse in practice, said Leila Sadat, professor of law and renowned expert on international criminal law.
Campus Author: The Japanese Supreme Court and Judicial Review
.ExternalClass p.MsoNormal, .ExternalClass li.MsoNormal, .ExternalClass div.MsoNormal
{margin-top:0in;margin-right:0in;margin-bottom:10.0pt;margin-left:0in;line-height:115%;font-size:11.0pt;font-family:Calibri;}
.ExternalClass .MsoChpDefault
{font-size:11.0pt;font-family:Calibri;}
.ExternalClass .MsoPapDefault
{margin-bottom:10.0pt;line-height:115%;}
@page WordSection1
{size:8.5in 11.0in;margin:1.0in 1.25in 1.0in 1.25in;}
.ExternalClass div.WordSection1
{page:WordSection1;}
David S. Law, JD, PhD, professor of law and professor of political science, has published a groundbreaking book on the Japanese judiciary and constitutional adjudication in Japan, titled The Japanese Supreme Court and Judicial Review (Gendaijinbunsha, 2013). Read more at http://law.wustl.edu/news/pages.aspx?id=9740.
Drones may violate international law
As President Obama gives a speech on national security — including defending U.S. use of drones to combat terrorism — Leila Sadat, JD, international law expert and professor of law at Washington University in St. Louis, argues that such targeted killing by unmanned planes may violate international humanitarian law. Legalities aside, she also questions whether it promotes U.S. interests abroad.
Atrocities Prevention Board could significantly change U.S. foreign policy
President Barack Obama recently announced the establishment of an Atrocities Prevention Board as part of his comprehensive strategy to prevent genocide and mass atrocities. “For the first time, the National Intelligence Council will prepare an estimate on the global risk of mass atrocities and genocide,” says Leila Nadya Sadat, JD, international law expert and director of the Whitney R. Harris World Law Institute at Washington University in St. Louis School of Law. “By sensitizing the diplomatic and intelligence communities to atrocities risk and systematizing responses to potential crises, the policies of the Atrocities Prevention Board could significantly change in U.S. foreign policy,” she says.
Legal training main obstacle to foreign law consideration in U.S.
Constitutional courts worldwide are increasingly turning to legal arguments and ideas from other countries for guidance and inspiration. But scholarly interest in the growing judicial use of foreign law paints a very misleading picture of the globalization of constitutional law, says David Law, JD, PhD, professor of law at Washington University in St. Louis. He says that for those who want to see the U.S. Supreme Court make greater and more sophisticated use of foreign law, encouraging its members or inviting them to additional conferences and gatherings is likely to have little impact. “At this point in time, the greatest obstacle to judicial comparativism in the United States is not the unwillingness of individual judges to consider foreign legal materials, it is the current political economy of the American legal education.”
Violence in Syria, Libya underscores need for convention on crimes against humanity
The violence against peaceful protesters in Libya and Syria drives home the need for an international convention for the prevention and punishment of crimes against humanity, says Leila Nadya Sadat, JD, international law expert and director of the Whitney R. Harris World Law Institute at Washington University School of Law. “The concerted efforts of the international community have helped to bring about a resolution of the Libyan situation, but the situation in Syria continues to deteriorate,” she says. “Reports of civilian roundups in Syria are reminiscent of Nazi roundups of the Jews during WWII. History shows that widespread human rights abuses lead to ethnic cleansing, crimes against humanity and even genocide.”
Despite pivotal post-WWII role in developing legal frameworks, United States appears threatened by international law
With over a dozen states considering banning Sharia (Islamic law) in their courts, laws governing other countries are facing increased scrutiny. “This is emblematic of U.S. fears about international law,” says Leila Nadya Sadat, the Henry H. Oberschelp Professor of Law and director of the Whitney R. Harris World Law Institute at Washington University in St. Louis. “International law has become a ‘whipping boy’ for the ills that are being felt because of globalization.” Sadat say that this is unfortunate because the United States proudly led the trial of the major German leaders at the end of World War II at Nuremberg. “In fact, the entire post-World War II framework of modern international law was, if not an American creation, at least American inspired and American driven,” she says.
Crimes Against Humanity project to draft international treaty
The Whitney R. Harris World Law Institute of the School of Law announced a two-year project to study the international law regarding crimes against humanity and to draft a multilateral treaty condemning and prohibiting such crimes. Leila Sadat, J.D., the Henry H. Oberschelp Professor of Law and director of the Harris Institute, recently convened the […]
View More Stories