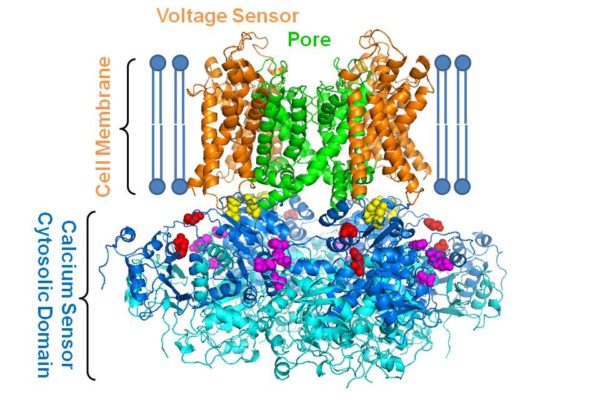
How molecular function affects high blood pressure, other diseases
By changing one small portion of a stimulus that influences part of one molecule’s function, engineers and researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have opened the door for more insight into how the molecule is associated with high blood pressure, autism and movement disorders.
The taste of love: what turns male fruit flies on
Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis have found a gene that seems to unleash the courtship ritual in male fruit flies. Males missing this gene are capable of courtship; they just have trouble getting started. Usually male fruit flies are “highly sexed,” to the point that they will court and mount “perfumed dummies,” decapitated females coated in waxy pheromones.
Solving the puzzle of the BK ion channel
A team of scientists at Washington University has discovered that an ion-channel mutation that causes epilepsy may do so by making part of the channel protein stiffer, so that the channel toggles open more easily. This is the first time that protein dynamics have been implicated in the functioning of an ion channel.
New math model of heart cell has novel calcium pathway
David Kilper/WUSTL PhotoProfessor Yoram Rudy (center), with Ph.D. student Yong Wang (left) and post-doctroal fellow Leonid Livshitz (right), with their ECGI system on a mannequin, comment on the cardiac data.Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis have developed the first mathematical model of a canine cardiac cell that incorporates a vital calcium regulatory pathway with implications for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats. Thomas J. Hund, Ph.D., post-doctoral researcher in Pathology ( in Dr. Jeffrey Saffitz laboratory) at the Washington University School of Medicine, and Yoram Rudy, The Fred Saigh Distinguished Professor of Engineering at Washington University, have incorporated the Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II (CaMKII) regulatory pathway into their model, improving the understanding of the relationship between calcium handling in cardiac cells and the cell’s electrical activity.