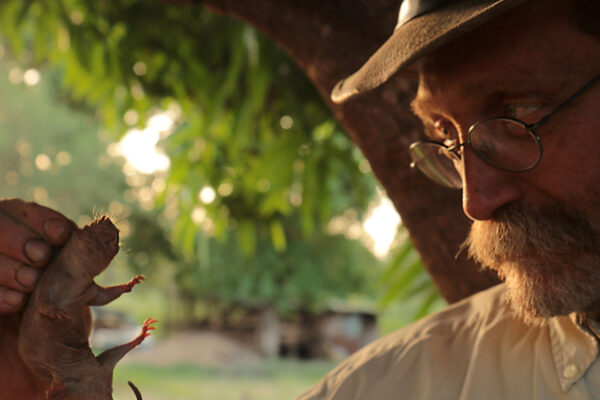
Tracking the migration of a naked mole rat
Stan Braude, a biologist in Arts & Sciences, published a new study in the African Journal of Ecology that considers the role of the moon in driving a particularly rare occurrence: the solo journey of a naked mole rat from one underground colony to start a new one.
Investigating water ice, space weathering on the Moon
Under a five-year, $7 million cooperative agreement led by Jeffrey Gillis-Davis, research associate professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, researchers will investigate fundamental questions at the intersection of space science and human space exploration.
On Apollo legacy, and why we should return to the moon
Humans have already learned much from the very first moon samples collected by the Apollo program astronauts. As NASA plans for its next manned mission by 2024, a leading lunar expert shares his science priorities for the return: “We need to learn how to live and work off Earth and beyond the low Earth orbit.”
New moon rock offers clues to moon’s formation
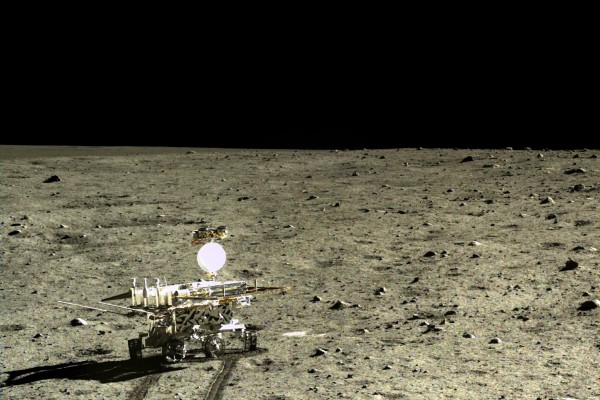
The Moon was never a fully homogenized body like Earth, analysis of Moon rocks made by the Chinese rover, Yutu, suggests. The basalts the rover examined are a new type, chemically different from those retrieved by the Apollo and Luna missions 40 years ago.
Water on moon topic of 2012 Robert M. Walker Distinguished Lecture Series
Maria Zuber, a professor of geophysics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, will deliver the fifth annual Robert M. Walker Distinguished Lecture at 7 p.m. Wednesday, Nov. 14, in Room 100 in Whitaker Hall on the Danforth Campus. During the free, public lectures, she will discuss new information about water on the moon.
Moon was created in giant smashup
It’s a big claim, but Washington University in St.
Louis planetary scientist Frédéric Moynier says his group has discovered
evidence that the Moon was born in a flaming blaze of glory when a body
the size of Mars collided with the early Earth.
WUSTL-led Moon mission is finalist for NASA’s next big space venture
Nearly 40 years after the Apollo astronauts first brought samples of the Moon to Earth for study, researchers from Washington University in St. Louis are leading an effort to return to the Moon for samples that could unlock secrets of the early Solar System. Known as MoonRise, the proposed Moon mission is one of three finalists now bidding to become NASA’s next big space science venture, a $650 million mission that would launch before 2019.
Larry Haskin honored with named crater on the moon
A crater on the moon has been named after the late Larry Haskin, Ph.D., who spent much of his career as a researcher in the WUSTL Department of Earth & Planetary Sciences.
Haskin honored with named feature on the Moon
HaskinA crater on the moon has been named after the late Larry Haskin, Ph.D., who spent much of his career as a WUSTL researcher in the Department of Earth & Planetary Sciences.
Earth’s orbit creates more than a leap year
The Earth’s orbital behaviors are responsible for more than just presenting us with a leap year every four years. According to Michael E. Wysession, Ph.D., associate professor of earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences, parameters such as planetary gravitational attractions, the Earth’s elliptical orbit around the sun and the degree of tilt of our planet’s axis with respect to its path around the sun, have implications for climate change and the advent of ice ages.
View More Stories