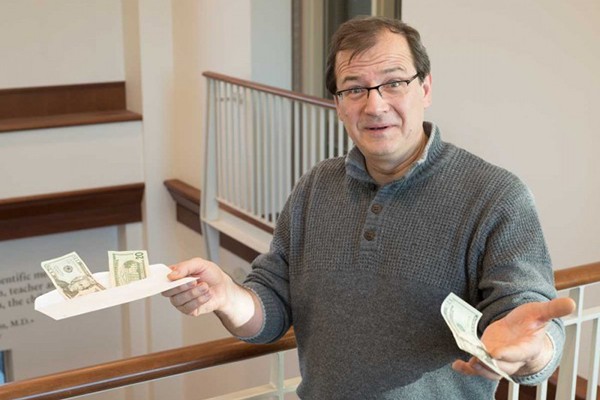
Genes influence choice between small rewards now or bigger ones later
Opting for smaller rewards immediately instead of waiting for bigger payoffs later is associated with problems such as impulsivity and addiction to food, drugs and alcohol. School of Medicine researchers led by Andrey Anokhin, PhD, are reporting that such decision-making tendencies have a genetic link to brain pathways that underlie those disorders.
$6.5 million to fund research, treatment of developmental disabilities
Researchers at the School of Medicine have received a five-year, $6.5 million grant to study the physiological underpinnings of developmental disabilities in children and to use the findings to search for novel ways to improve such children’s lives. The grant renews funding for the university’s Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Research Center (IDDRC), which is directed by John N. Constantino, MD (left) and Bradley L. Schlaggar, MD, PhD.
Trial to study if smoking-cessation therapy can be tailored to smokers’ DNA
A School of Medicine study may aid efforts to tailor smoking-cessation treatments to individual cigarette smokers. Researchers are recruiting 720 smokers whose DNA samples, from saliva, will be analyzed to identify genetic variations that influence smoking behavior, lung cancer risk and the effectiveness of smoking-cessation treatments.
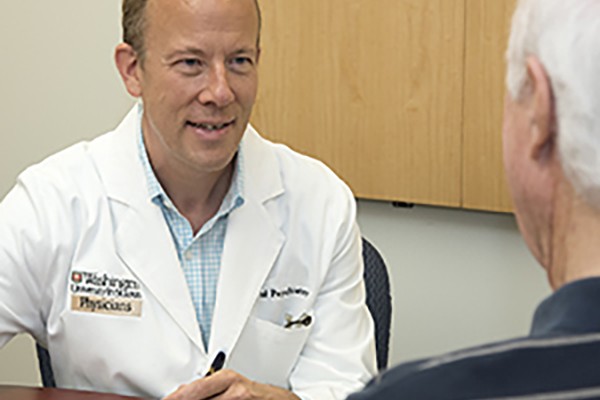
On the rise: Painkiller abusers who also use heroin
Drug abusers are not completely abandoning prescription opioids for heroin, according to School of Medicine researchers. Instead, many use the two concurrently based on their availability. The researchers’ findings also reveal regional variations in the use of heroin and prescription painkillers.
Loss of support cells in brain may inhibit neuronal development
Shedding light on possible contributors to autism, schizophrenia and other neuro-psychiatric disorders, School of Medicine researchers have found that a type of support cell in the brain, called an astrocyte, may play a role in the ability of neurons to communicate.
On Twitter, hookah smoking seen as positive
Positive mentions on Twitter about hookah smoking may promote the assumption that it is less harmful than smoking cigarettes even though the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that hookah smoking has many of the same harmful toxins and carries the same health risks, according to new research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis led by Melissa J. Krauss, seen here with a hookah pipe.
$15 million funds research to help older adults prevent cognitive decline
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, led by Eric J. Lenze, MD, have received a $15 million grant to study strategies — including exercise, health education, meditation and yoga — aimed at helping older adults prevent or reverse typical age-related cognitive declines.
Obituary: John W. Olney, 83, professor of psychiatry and neuropathology
John W. Olney, MD, the John P. Feighner Professor of Psychiatry and professor of pathology and immunology, died Tuesday, April 14, 2015 at his home in St. Louis after a battle with lung cancer and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). He was 83.
Gene variant linked to smoking longer, getting lung cancer sooner
Smokers with a specific genetic variation are more likely to keep smoking longer than those who don’t have the gene variant. They’re also more likely to be diagnosed with lung cancer at a younger age, according to new research from Laura Jean Bierut, MD (left), and Li-Shiun Chen, MD, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
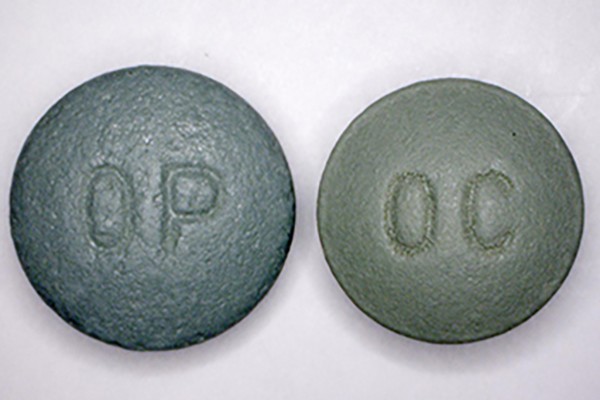
Harder-to-abuse OxyContin doesn’t stop illicit use
A reformulation of OxyContin (left) that makes it less likely to be abused than the older formulation (right) has curtailed the drug’s illicit use. But researchers at the School of Medicine have found that a significant percentage still abuse the drug despite package labeling that emphasizes its abuse-deterrent properties.
View More Stories