Back to the beginning
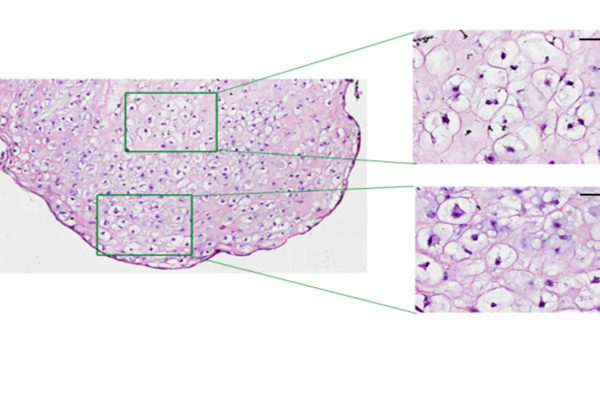
As scientists try to find therapy options to fight back and neck pain, considerable interest exists in harnessing stem cells to restore nucleus pulposus, the chief material in discs. Previous research shows human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) can express markers for a wide variety of cells, including those that secrete NP. A collaborative team of scientists at Washington University has developed a new process to generate NP-like cells from hiPSCs.
Gut microbes’ metabolite dampens proliferation of intestinal stem cells
New research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates stem cells located in “pockets” in the intestine avoid contact with a prominent metabolite produced by beneficial microbes living in the gut. That metabolite – butyrate – restricts the proliferation of stem cells, potentially hampering the intestine from repairing itself after an injury or damage.
Stomach cells naturally revert to stem cells
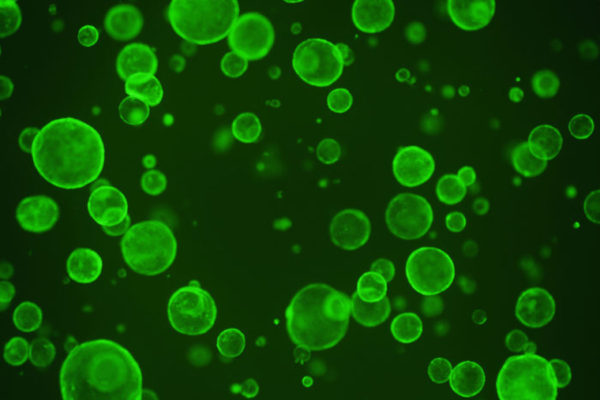
Scientists from the School of Medicine and in the Netherlands have found that a class of specialized cells in the stomach reverts to stem cells more often than researchers had thought. One or more chief cells, which normally make digestive juices in the stomach, have changed into a stem cell in the image shown.
Washington People: John F. DiPersio
Every year, Siteman Cancer Center hosts a gathering for former bone marrow transplant patients, their families and the staff who helped care for them. It’s a celebration of survival. And every year, John F. DiPersio, MD, PhD, chief of the Division of Oncology, looks out over the audience and marvels. From the lab to the clinic, DiPersio’s work is guided by his commitment to his patients.
Protein critical to gut lining repair
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine
in St. Louis have identified a protein essential to repairing the
intestine’s inner lining.
Pediatric tumors traced to stem cells in developing brain
Stem cells that come from a specific part of the developing brain help fuel the growth of brain tumors caused by an inherited condition, researchers, including David H. Gutmann, MD, PhD, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report.
Clues found to way embryonic kidney maintains its fleeting stem cells
Studying mice and humans, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and their collaborators in Paris have identified two proteins that are required to maintain a supply of stem cells in the developing kidney. The work is a small step toward the future goal of growing kidney stem cells in the lab.
Zebrafish regrow fins using multiple cell types, not identical stem cells
What does it take to regenerate a limb? Biologists have long thought that organ regeneration in animals like zebrafish and salamanders involved stem cells that can generate any tissue in the body. But new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has shown that the individual cells in a regenerating limb retain their original identities and only give rise to more of their own kind.