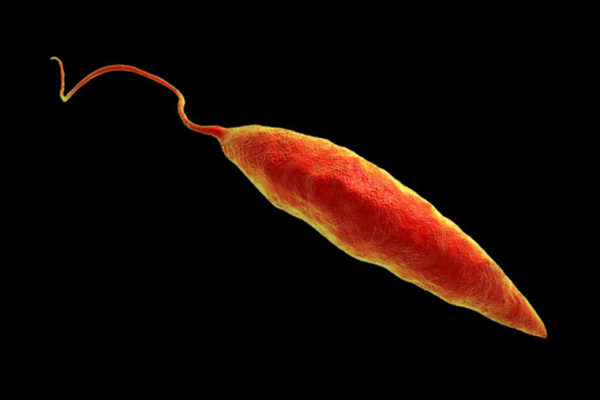
Viruses exacerbate disease caused by Leishmania parasite
Washington University School of Medicine’s Stephen Beverley found that viruses hidden inside the parasite Leishmania worsen disease caused by the parasite. Now, an evolutionary survey of the viruses in related parasites suggests that Leishmania’s viruses may have helped it make the jump from infecting insects to infecting vertebrates.
Treatment failure in parasite infection tied to virus
Two new studies explain why some parasite
infections, such as those common in developing countries, sometimes
can’t be cured with standard treatments. The research shows the parasite Leishmania — which infects 12 million
people worldwide — often harbors a virus that helps the parasite
survive treatments.
Virus, parasite may combine to increase harm to humans
A parasite and a virus may be teaming up in a way that increases the parasite’s ability to harm humans, scientists at the University of Lausanne in Switzerland and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report this week in Science.
Discovery lets scientists seize controls of South American parasite
Scientists battling Leishmania, a parasite second only to malaria in the number of deaths it causes, have identified an important vulnerability in the genetic code of one major parasite strain.
Cancer drugs may help stop major parasite
A parasite estimated to afflict as many as 12 million people worldwide relies on a family of genes that should make it vulnerable to compounds developed to treat cancer and other disorders, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found.