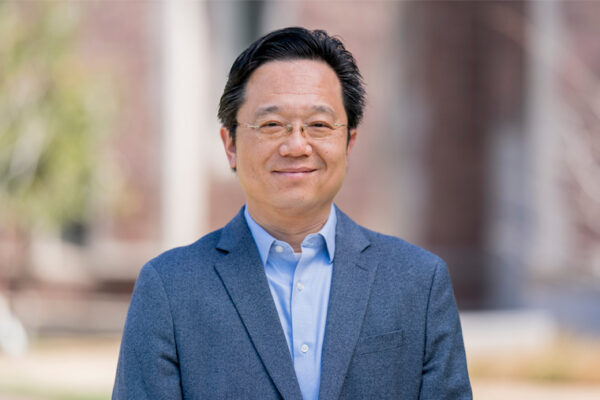
Chenyang Lu, the Fullgraf Professor of computer science and engineering in the Washington University in St. Louis McKelvey School of Engineering, is combining artificial intelligence with data to improve patient care and outcomes.

But he isn’t only concerned with patients, he is also developing technology to help monitor doctors’ health and well-being.
The Lu lab presented two papers at this year’s ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, both of which outline novel methods his team has developed — with collaborators from Washington University School of Medicine — to improve health outcomes by bringing deep learning into clinical care.
For caregivers, Lu looked at burnout, and how to predict it before it even arises. Activity logs of how clinicians interact with electronic health records provided researchers with massive amounts of data. They fed this data into a machine learning framework developed by Lu and his team — Hierarchical burnout Prediction based on Activity Logs (HiPAL) — and it was able to extrapolate meaningful patterns of workload and predict burnout from this data in an unobtrusive and automated manner.
Learn more about the team’s work on the engineering website.
When it comes to patient care, physicians in the operating room collect substantial amounts of data about their patients, both during preoperative care and during surgery — data that Lu and collaborators thought they could put to good use with Lu’s deep-learning approach: Clinical Variational Autoencoder (cVAE).
Using novel algorithms designed by the Lu lab, they were able to predict who would be in surgery for longer and who was more likely to develop delirium after surgery. The model was able to transform hundreds of clinical variables into just 10, which the model used to make accurate and interpretable predictions about outcomes that were superior to current methods.
Learn more about the team’s findings on the engineering website.
Lu and his interdisciplinary collaborators will continue to validate both models, hopeful that both bring the power of AI into hospital settings.
The McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis promotes independent inquiry and education with an emphasis on scientific excellence, innovation and collaboration without boundaries. McKelvey Engineering has top-ranked research and graduate programs across departments, particularly in biomedical engineering, environmental engineering and computing, and has one of the most selective undergraduate programs in the country. With 140 full-time faculty, 1,387 undergraduate students, 1,448 graduate students and 21,000 living alumni, we are working to solve some of society’s greatest challenges; to prepare students to become leaders and innovate throughout their careers; and to be a catalyst of economic development for the St. Louis region and beyond.