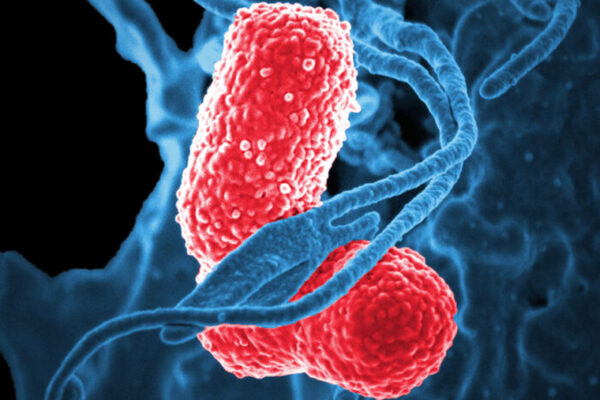
In the U.S., the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae is a common cause of urinary tract infection, bloodstream infection and pneumonia. While infections with the bacterium can be easily treated in some, Klebsiella has a dangerous flip side: It also is frequently resistant to antibiotics, making it extraordinarily difficult to treat in others. About half of people infected with a hypervirulent, drug-resistant strain of the bacterium die.
Scientists are working on vaccines for Klebsiella, but the optimal vaccine design is still unknown. However, a new study in mice by scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Omniose, a St. Louis startup company specializing in vaccine production, provides critical data that could be key to developing an effective vaccine for Klebsiella. The findings, published in PLoS Pathogens, are a step toward taming the superbug.
“When you think about the bugs that can be resistant to almost all antibiotics — the scary superbugs in the news — a lot of them are strains of Klebsiella,” said the study’s senior author, David A. Rosen, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of pediatrics and of molecular microbiology at Washington University. “For a long time, the bacterium wasn’t even a pressing issue. But now it is, due to an explosion in antibiotic-resistant Klebsiella. Our goal is to diminish Klebsiella’s superbug status by developing a vaccine before hypervirulent or resistant strains sicken and kill even more people.”
Hypervirulent Klebsiella strains have spread globally, often causing community-acquired infections.
In the U.S., Klebsiella infections primarily occur in health care facilities where medically vulnerable patients are immunocompromised, require long courses of antibiotics to treat other conditions, have chronic diseases, or are elderly people or newborns. “But now we’re seeing the emergence of hypervirulent strains dangerous enough to cause serious disease or death among healthy people in the community,” Rosen said.
Most concerning among scientists are the strains of Klebsiella impervious to carbapenems, a class of broad-spectrum antibiotics used to treat the most severe bacterial infections. For this reason, the World Health Organization and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have identified carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella as an urgent threat to public health.
The rod-shaped bacterium is immobile and, like chocolate-covered candies, encapsulated in sugar coatings. In the new study, researchers created two experimental vaccines based on two different sugars, or polysaccharides, on Klebsiella’s surface: the terminal sugars on lipopolysaccharide, called O-antigen, and a capsular polysaccharide, or K-antigen. Since sugars by themselves tend to produce weak immune responses, the researchers linked each of the sugars to a protein to boost the immune response, creating so-called conjugate vaccines. Sugar-protein conjugate vaccines have proven successful in combating several bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae, the most common cause of pneumonia. Historically, this connection between the sugar and protein carrier has been achieved using synthetic chemistry in a test tube; however, the vaccines created for this study are called bioconjugate vaccines, because the researchers connected the sugar to the protein all within an engineered bacteria system.
Once the vaccines were created, the researchers tested the experimental bioconjugate vaccines’ ability to protect mice from disease caused by Klebsiella.
“It turned out that the capsule vaccine was far superior to the O-antigen vaccine,” said the study’s first author, Paeton Wantuch, a postdoctoral associate in Rosen’s lab. “Mice that received the capsule vaccine were significantly more likely to survive Klebsiella infection in their lungs or their bloodstream than mice that received the O-antigen vaccine.”
Both vaccines elicited high levels of antibodies against their respective targets. But the antibodies against the O-antigen just weren’t as effective as the ones against the capsule. In some strains of Klebsiella, the O-antigen may be obscured by other sugars, so the antibodies that target the O-antigen cannot make contact with their target.
“Our findings suggest that we may also need to include the capsule-based antigens in vaccine formulations developed against Klebsiella,” Rosen said. “This is why it’s so important for us to continue studying antibody-antigen interactions in the different strains, with the goal of identifying the ideal vaccine composition for clinical trials soon. The need has never been more imperative, especially as Klebsiella’s drug-resistant, hypervirulent strains become stronger, bolder and more dangerous to human health.”
Paeton WL, Knoot CJ, Robinson LS, Vinogradov E, Scott NE, Harding CM, Rosen DA. Capsular polysaccharide inhibits vaccine-induced O-antigen antibody binding and function across both classical and hypervirulent K2:O1 strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLOS Pathogens. Published online May 5, 2023. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011367
This work was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), grant numbers R41 AI167078-01 and R42 AI165116-01A1; the Children’s Discovery Institute of Washington University; WashU’s W.M. Keck Postdoctoral Fellowship in Biomedical Research; St. Louis Children’s Hospital; the Australian Research Council (ARC) Future Fellowship, FT200100270; ARC Discovery Project Grant, DP210100362. Co-authors Cory J. Knoot, Lloyd S. Robinson and Christian M. Harding have a financial stake in Omniose, a for-profit entity developing bioconjugate vaccines using patented technology derived from the data presented in this and other published manuscripts.
About Washington University School of Medicine
WashU Medicine is a global leader in academic medicine, including biomedical research, patient care and educational programs with 2,800 faculty. Its National Institutes of Health (NIH) research funding portfolio is the third largest among U.S. medical schools, has grown 52% in the last six years, and, together with institutional investment, WashU Medicine commits well over $1 billion annually to basic and clinical research innovation and training. Its faculty practice is consistently within the top five in the country, with more than 1,800 faculty physicians practicing at 65 locations and who are also the medical staffs of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children’s hospitals of BJC HealthCare. WashU Medicine has a storied history in MD/PhD training, recently dedicated $100 million to scholarships and curriculum renewal for its medical students, and is home to top-notch training programs in every medical subspecialty as well as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and audiology and communications sciences.